
GIS software has been empowering the electric utility industry for decades. It provides a robust framework for asset and workforce management as well as tools for planning and analysis. Today, the landscape is filled with desktop solutions like those from ESRI, open-source software like QGIS, but also a host of online GIS solutions.
In this article, we’ll give you an overview of the uses of GIS for electric utilities and provide a real-life example from an electricity distribution company. Also, we’ll show you how to use GIS Cloud, our own solution for field operations and workforce collaboration in electric utilities.
Table of contents:
• Using GIS in Electric Utilities
• Asset Inventory and Infrastructure Insights
• Collaborating and Sharing Geospatial Data
• The GIS Cloud Solution Workflow
• 1. Creating Field Data Collection Projects
• 3. Editing Data and Overseeing Fieldwork
• 4. Sharing Data With Clients, Subcontractors and Managers
• Case Study – ENUGU Electricity Distribution Company
• Key Benefits of GIS for Electric Utilities
Using GIS in Electric Utilities
You could say that a geographic information system is essential for electric utility companies. It provides the foundational layer of technology for effective asset management as well as regulatory compliance. Companies use GIS for multiple purposes, from managing field operations to performing spatial analysis. Let’s dive in and learn how to utilize GIS and especially online GIS apps in electric utilities.
Asset Inventory and Infrastructure Insights
It’s crucial to have an accurate asset inventory with electric poles, transformers, cable lines, substations and other electric utility assets properly mapped. GIS allows you to manage the asset data a lot easier and enables you to take insight from the infrastructure.
With a properly set up GIS suite, you can get amazing insights from infrastructure data by:
- Analyzing usage patterns
- Recognizing problems and risks like power outages
- Having oversight about energy consumption
- Finding potential threats to the power grid
- Managing utility asset repairs
Before you start with the analysis, it’s essential to have quality data; you need to know the condition of assets, their locations and other info. Which brings us to the next point.
Optimizing Field Operations
Field operations in electric utilities are usually about mapping the infrastructure and performing routine inspections. But to get high-quality field data, you need an effective field workflow and a field crew equipped with surveying equipment or data collection apps.
In most companies, the daily workflow starts with printing inspection forms and maps of the survey area. The field crews then go on to record the locations of assets and perform inspections. The field data then makes its way to the office where it’s transcribed to a desktop GIS or AutoCAD software. This is a typical paper-based workflow with many drawbacks like illegible inspection forms, uncredited asset photos, lost paper forms and so on. To improve the workflow, we strongly suggest using online GIS apps to make the workflow paperless and more efficient.

To get there, you’ll need to use data collection apps for surveys and inspections, as well as Cloud GIS web apps to manage the data. Replace the paper maps with interactive mobile apps that have the needed infrastructure data. Utilize mobile data collection apps as a substitute for messy paper forms. And finally, end the data transcribing for good by using web apps that are in sync with mobile data collection apps.
Now you understand how to use GIS to improve your field operations, but what about enhancing collaboration between subcontractors, clients and company management?
Collaborating and Sharing Geospatial Data
To get the most out of GIS technology, it’s best to connect everyone in the workflow: field workers, engineers, managers, decision makers and clients. The web-based GIS apps allow you to keep your data centralized in one place enabling, everyone to collaborate over the same geospatial dataset.
When the field workers collect data, it immediately populates an online map. That allows the office team to give direct feedback regarding the quality of data. It also enables the management to track the productivity for individual workers.
After a survey is done, it’s time to share the data with other departments, clients or subcontractors. Here you can get a lot of help from online maps and being able to share them with practically anyone involved in the project. We’ll get into details in the next chapter where we’ll show you how to share geospatial data with GIS Cloud apps.
The GIS Cloud Solution Workflow
In this chapter, we’ll show you how to use GIS Cloud apps for projects in electric utilities. The apps are designed to support your entire field operations workflow, from collecting field data to automating tedious office tasks. First, we’ll show you how to create a surveying project in the Mobile Data Collection Portal.
1. Creating Field Data Collection Projects
Before you can start collecting data, you need to create a project (survey form) in the Mobile Data Collection Portal (MDCP). There you can create and edit any number of mobile forms and manage the collected field data.
Creating a form is easy: name the form, choose what you’re collecting (point, line or polygon), add all the required fields and that’s it.
The types of fields you can add to a mobile form:
- Standard items (text, number, date & time, checkboxes…)
- Media (photos, audio recordings, QR/Barcode)
- Device and user (user name, device ID, device version…)
- Location (latitude, longitude, altitude, GPS heading, accuracy…)
There are a lot of features you can use to create a form that suits your needs. You can specify any field as required, read-only, persistent or autofill. Also, you can create dependent fields that allow you to manage sets of dependencies between fields. When a field is dependent, it will only be available if the state of the parent field satisfies the right rule. If the rule is not met, it will not be possible to view or edit the dependent form field.
Here’s how it looks when creating a mobile form: 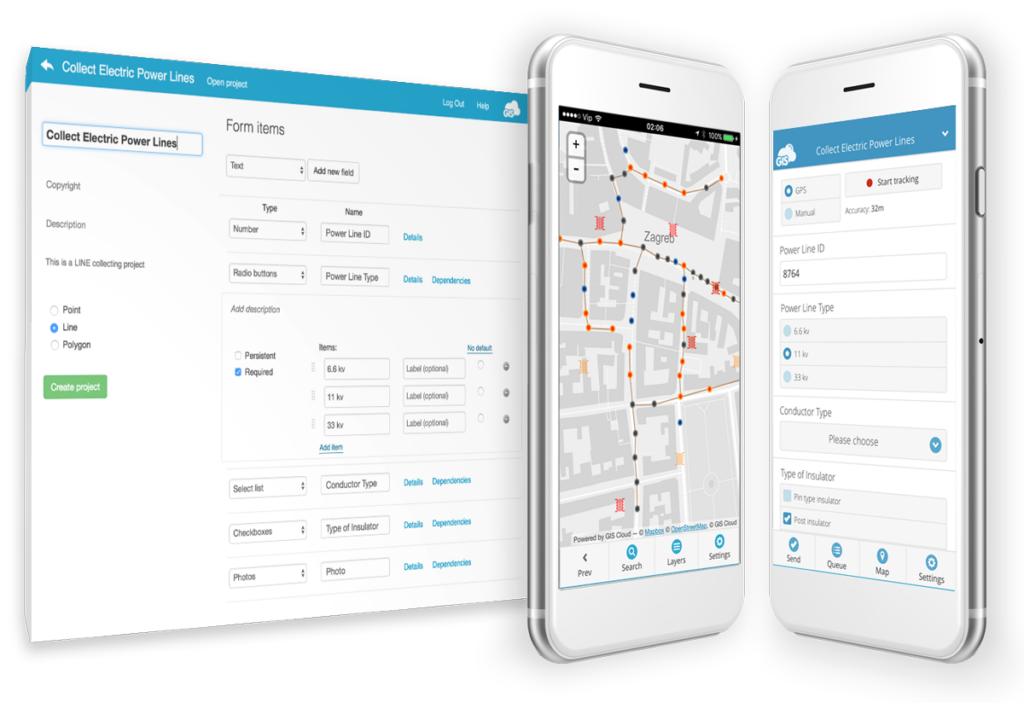
To start collecting field data, you need to share the project with your field workers. Just open the project, share to a particular username and assign the desired privileges (View, Share, Edit, Export, Collect and/or Update).
2. Collecting Field Data
Now that you’ve created a mobile form and assigned it to your field workers, it’s time to start collecting data with the Mobile Data Collection app. It’s easy as it gets, choose the desired MDCP project (form), fill out the form and press send. The data and the location will instantly show in the MDCP web app and Map Editor.
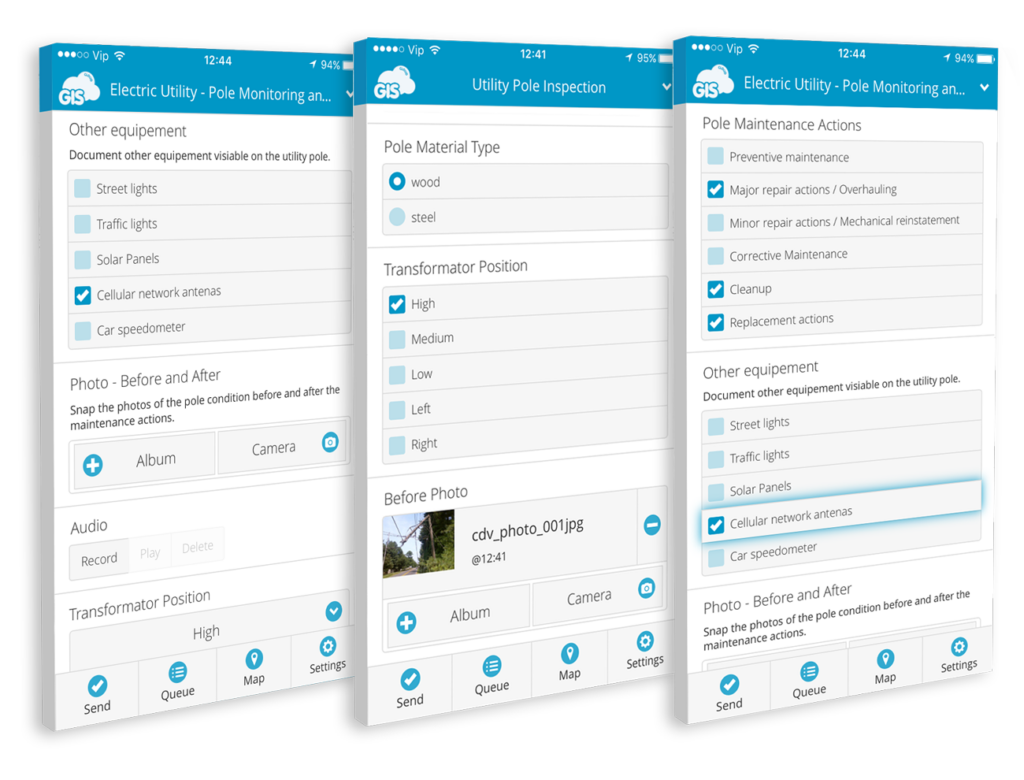
If you find yourself in an area with a weak GPS signal, it’s best to use the pinpoint tool. It allows you to retain good accuracy by pinpointing the location on the map.
The MDC app works offline as well in case you lose internet connection. The collected data waits in the queue for the mobile phone to connect to the internet and then pulls the data online.
Let’s wrap up with the field workflow and take a look at how GIS Cloud apps can help you improve efficiency at the office.
3. Editing Data and Overseeing Fieldwork
GIS Cloud apps enable you to digitize your office workflow. There’s no need to transcribe paper forms or print maps, it’s all in one place, always available. We recommend using the Map Editor for in-office tasks like editing field data, analysis, and sharing maps and reports.
Map Editor is the central app in the GIS Cloud suite. It supports a number of vector and raster formats, rich GIS symbology and it has built-in collaboration capabilities which allow real-time editing and sharing. Map Editor is equipped with a file and database manager, and it integrates easily with ArcGIS and QGIS.
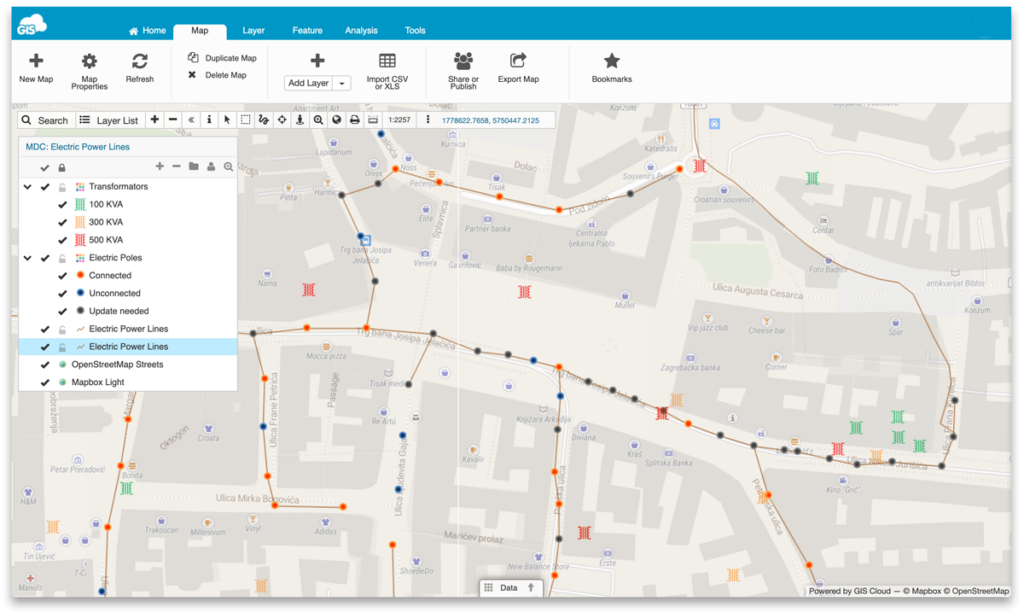
You can also track the progress of your survey. The data collected in the field instantly populates the map in the MDCP or the Map Editor app, giving you real-time oversight over what’s going on in the field. It enables you to monitor the field data quality, review the collected data and quickly provide feedback to workers or subcontractors.
It’s easy to track productivity, as well. If you want to know how many assets each of the field workers collected, create a filter in the data grid and export the data to CSV format.
4. Sharing Data With Clients, Subcontractors and Managers
To share data with clients, you probably use Dropbox, flash drives, or DVDs, making it a messy process with data scattered all around. To fix this issue, it’s best to centralize all of your data by uploading it to the GIS Cloud and using the Map Viewer app to give access to your clients, subcontractors or management.
The Map Viewer makes collaboration on large datasets possible. Everyone involved has access to the same dataset and can filter and export the data. No need to import data to desktop GIS software like ArcGIS or QGIS just to see how it looks.
If you need a branded interface when sharing data with clients, it’s possible to white label your Map Viewer with custom colors and your logo.
Here’s an example of a white-labeled interface from our clients the ENUGU Electricity Distribution Company:
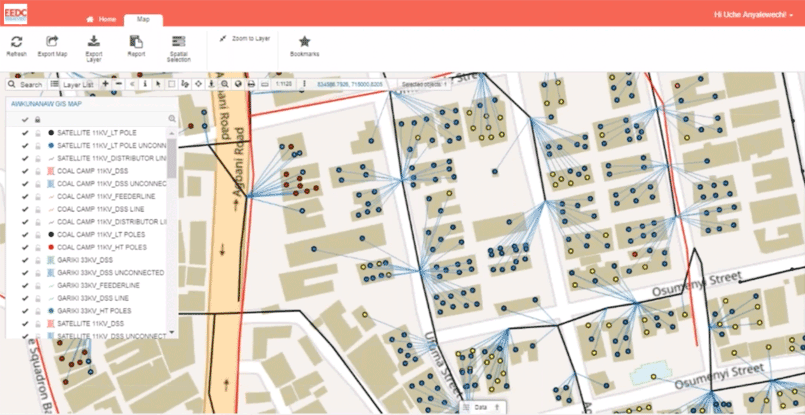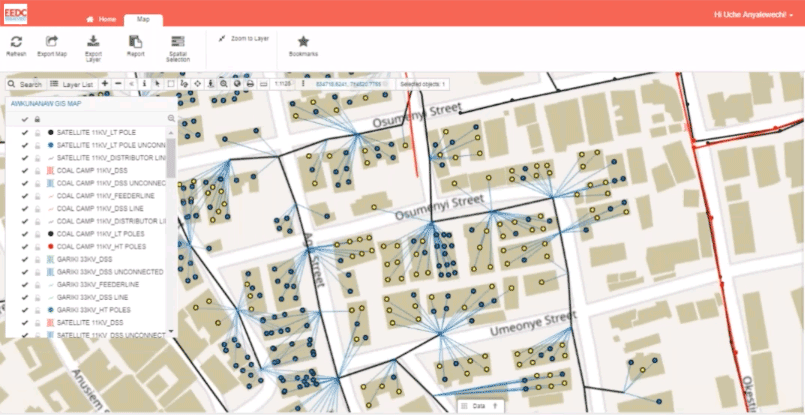
Case Study – ENUGU Electricity Distribution Company
Now that you know the basics of how GIS Cloud apps work, it’s best you see them in action. We bring you a use case from ENUGU, the largest electricity distribution company in Nigeria. The company had serious problems with electricity theft and were losing vast amounts of resources from illegal connections to the grid. To tackle the problem, they planned to embed a smart meter into every household. But first of all, the company needed to map the electricity distribution network and index the customers.
To map out the electric poles, transformers, substations as well as customer locations, they deployed Mobile Data Collection apps to 150 field workers. The field teams were equipped with pre-made mobile forms for each type of asset (e.g. utility pole inspection form) to make the data collection and asset inspections as fast as possible.
To monitor the field data quality, the operations managers from ENUGU used the Map Editor app to review the data for each utility asset. If the data didn’t suffice, they could quickly give feedback to workers and subcontractors. The Map Editor also allowed them to monitor the progress of the survey in real time and for individual workers.
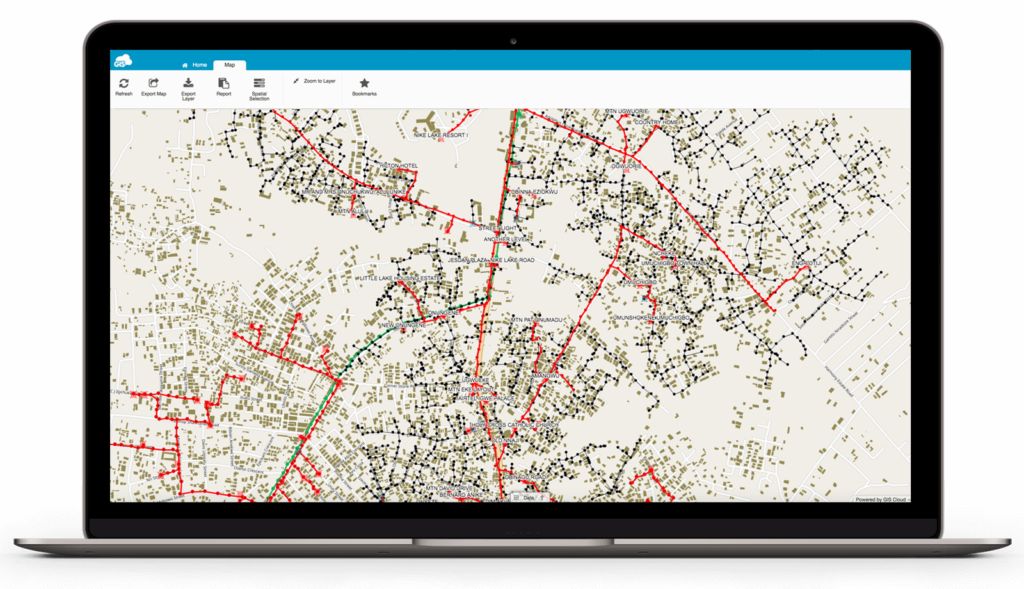
The Map Viewer app was of great use to the project as it allowed the stakeholders to view and share maps and field data online. The subcontractors could share the completed maps for review to the ENUGU supervisors.
Learn more about how ENUGU utilized GIS Cloud to optimize the cost of field operations in this comprehensive case study.
Key Benefits of GIS for Electric Utilities
There are many ways your field operations and overall collaboration can benefit from GIS and Cloud GIS apps. We’ve mentioned a lot of them in the article but here’s a quick recap:
- Cutting Costs by Going Paperless
- Real-time insight – instantly available
- Instant feedback from the field
- React instantly to a project issue
- Maintenance, quality control, plan ahead
- All in one solution – upload data / collect, sharing, publishing, collaboration
- Only get the apps you need this month – pay as you go
Regarding the last point about the pay-as-you-go model, some of the online GIS providers have a pricing model that allows you to upscale or downscale according to your needs. For example, here at GIS Cloud, you only pay for what you use. If the project scope changes, you can easily unsubscribe or subscribe for new licenses.
Interested in using GIS Cloud for electric utilities? Sign up for the free trial. You’ll have 30 days to test the apps and see if they fit your field workflow. If you want someone to show you around and propose a possible GIS solution contact our sales consultants.






